Get 10% Off*, Use Code: RSHS25
Get 10% Off*, Use Code: RSHS25

Introduction | Surgery | Recovery | Complications
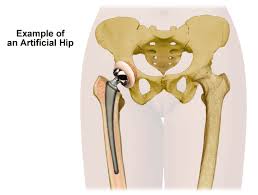
Severe pain in the hip joint, long-term stiffness and restricted mobility plus impaired quality of life may call for surgery to replace the hip joint with an artificial part. As the term suggests, hip replacement is a surgical procedure involving the substitution of the diseased or damaged hip joint with prosthesis to allow normal mobility of the joint. This procedure is also known as arthroplasty and is gradually becoming more and more common even among people below the age of 60. It is fast becoming a routine procedure and being performed on approximately one million people each year the world over.
There are several medical conditions which may require hip replacement surgery of which two are the most common - osteoarthritis and severe arthritis. Other reasons could be bone tumors and osteonecrosis, which is a disease caused by temporary or permanent loss of blood supply to the bones. A hip fracture may also be a criterion. Stiffness, pain and immobility are a result of these conditions because of which hip replacement may be considered a likely solution.
Before deciding on surgery, your doctor will first try other treatments like exercise and medicines. Only if these are found to not work then will surgery be advised. Your doctor will also evaluate the quality of your life and try to ascertain whether the pain and stiffness in your hip is interfering with your daily activities.
Before opting for this surgery, you may need to have detailed discussions with your orthopedic surgeon about what this procedure will involve. This is considered a crucial surgery so a complete evaluation is necessary. For instance, your doctor will mull over several factors before any decision is taken. Your health will be an important consideration. Your overall health and activity level will be even more crucial than age for this surgery to be a success. To be a good candidate for hip replacement you must be of sound health.
Age is no longer considered an issue for hip replacement surgery. In the earlier days, only elderly people, over 60 years of age, would be asked to go in for hip replacement but today, more and more young patients are being recommended for this procedure. It is believed that if the correction is done while young, there are better chances of complete and faster recovery. Doctors now say that before advanced joint damage can occur you should have hip problem corrected for better outcome and improved quality of life. The artificial joint that is used these days is of high quality and can withstand more stress and strain than before and hence, is suitable for the more hectic lifestyle of younger people.

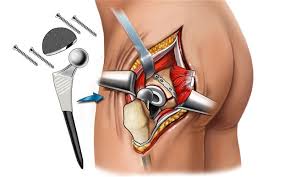
A hip replacement procedure usually takes 1-2 hours and may either be a regular surgery done under general anesthesia or, in case of patients younger than 50, be minimally invasive with a small incision and quick recovery period. It could also be conducted under regional anesthesia. All this will depend on your surgeon who will evaluate your health status and speak to you about your personal preference.
The surgery will involve a cut over the side of the hip through the muscles for removal of the damaged bone tissue and cartilage from the hip joint and replacing the ball at the upper end of the thighbone or femur and acetabulum with new, artificial parts. In a total joint replacement surgery, the ends of both bones are replaced.
The artificial parts comprise of two basic components – ball and socket. The ball is made of polished metal or ceramic while the socket is made of metal, ceramic or plastic/polyethylene. These parts may be attached to the existing bone with cement or a porous coating. Cement acts as glue and is used to join an artificial part made of cement to the bone. Non-cement parts are joined to the bone using the porous coating whose openings are, over time, filled with new bone growth thus fixing the bone to the artificial joint.
Cement is more popular and may be used for older and less active people while non-cement prostheses, which were introduced only in the late 1970s, are more common among younger and more active people. Non-cement prostheses limit activities of the patient for up to three months and may also cause pain in the thighs in the months following the surgery.
The time spent in the hospital after the surgery is usually between 3 to 5 days and during this period, you will be allowed restricted movement. It will take several weeks before you are completely mobile and able to walk without a walker or crutches. Total rehabilitation after surgery will take approximately six months. During the recovery period, you will be told to not put your full weight on your legs and may also require the services of a physical therapist to teach you to exercise. While following your doctor’s advice on precautions, you may, in a few weeks time, start to gradually limp back to normal life.
Hip dislocation is the most common problem after hip replacement surgery. Though now advances in technology have led to an improvement in the procedure and rate of success, sometimes the patient may experience an inflammatory reaction to the artificial joint which may see tiny pieces breaking off from the main part and getting absorbed by the surrounding tissue. This may require revision surgery or use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Other complications include blood clots, infection and extra bone growth.
Doctors try to evade surgery and prefer to try out all other less invasive options first. When it is found that nothing works and that the pain is severe and quality of life is suffering then you may be told to go for hip replacement. However, anyone cannot go in for it. Those people who have poor immunity and are easily prone to infection cannot opt for this procedure for various reasons. Also it is not advisable for people suffering from muscle weakness and with Parkinson’s disease to go for hip replacement. If you do not have enough bone or strong bone to support an artificial hip then too you will be advised against this surgery.
Disclaimer: All content found on our website, including images, videos, infographics and text were created solely for informational purposes. Our content should never be used for the purpose of diagnosis or treatment of any medical conditions. Content shared on our websites is not meant to be used as a substitute for advice from a certified medical professional. Reliance on the information provided on our website as a basis for patient treatment is solely at your own risk. We urge all our customers to always consult a physician or a certified medical professional before trying or using a new medical product.